
Science + Tech – Articles, Analysis, Opinion
Displaying 1 - 25 of 3563 articles

Nobody wants to see an accident involving flammable, corrosive or radioactive material. But understanding the rules put in place to prevent these accidents isn’t easy.

From synthetic fabrics to car exhaust to wildfires, exposure to environmental pollutants push the skin microbiome to adapt in ways that reduce its ability to protect the skin.

If the US wants to protect young people from misinformation and foreign influence, focusing on TikTok is barking up the wrong tree.

Ethics is often neglected in engineering education, two researchers write, despite mounting questions about how to responsibly design artificial intelligence programs.

AI chatbot makers’ restrictive use policies hinder people’s access to information.

From kimchi to kombucha and sauerkraut to sourdough, many traditional food staples across cultures make use of fermentation. And these variations are reflected in your microbiome.

Saturn’s moon Enceladus has geysers shooting tiny grains of ice into space. These grains could hold traces of life − but researchers need the right tools to tell.

Whether people are hunters can have a big effect.

There is no shortage of horror stories about online shaming, but it’s not always a bad thing. It comes down to who is doing the shaming and how cohesive the online community is.

New research found a way to both improve the accuracy of deepfake detection algorithms while also enhancing fairness.

There are many ways to kill microbes that cause dangerous infections. Combining genetic screening with machine learning can help researchers identify new antimicrobials.

Where specialized algorithms fail to classify star-borne pulses, human volunteers with just a little training can step in.
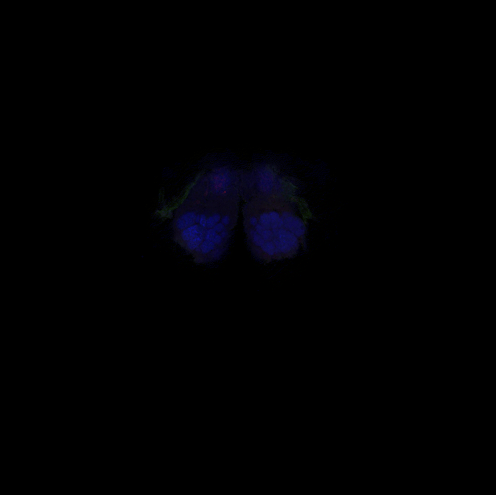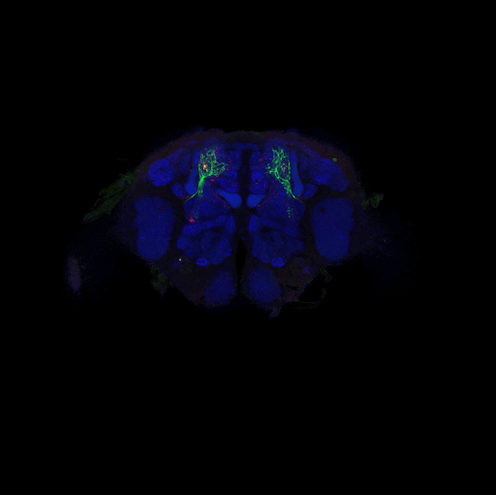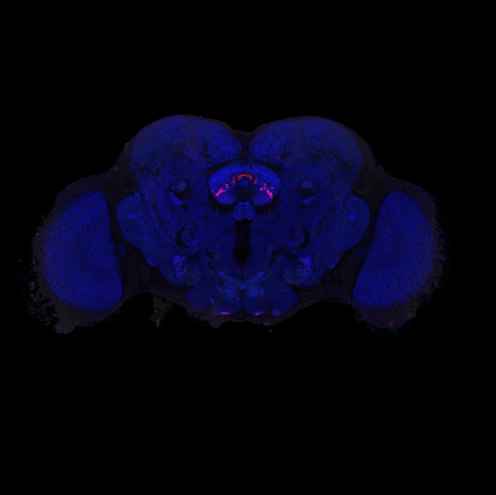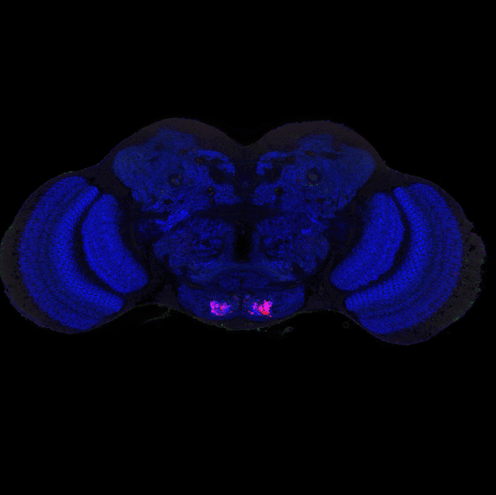
Studying the human brain is difficult because of its vast and intricate network of neural connections. The fruit fly offers a simpler but similar model that researchers can more easily map.

Here’s a game: Tell a friend to give you any number and you’ll return one that’s bigger. Just add ‘1’ to whatever number they come up with and you’re sure to win.

AI has the potential to diminish the human experience in several ways. One particularly concerning threat is to the ability to make thoughtful decisions.

Historians are working to shine a light on Alice Ball’s legacy and contributions to an early treatment of a dangerous and stigmatizing disease.

Functional precision medicine works to take the guesswork out of deciding which drug to try next for patients with cancers that don’t respond to standard treatments.

No treatments are currently available to cure Parkinson’s disease. Better understanding the genetic foundation of this condition can help researchers find ways to slow or halt its progression.

Most infection prevention guidelines center on the hospital environment rather than the patient. But the source of antibiotic-resistant microbes is often from the patient’s own body.

Use-inspired research goes beyond translational research to build lasting connections between researchers and communities.
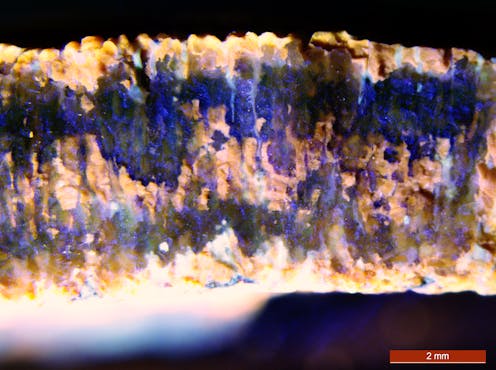
Calcite, the material making up fossilized eggshells, may preserve amino acids better than bone.

Measuring the concentration of radioactive elements in a single, sand-size crystal reveals the growth of the Himalayan mountain range over time.

This bias in science journalism seems not to be due only to pragmatic concerns about time zones or the language spoken in the country where the scientist is based.

A civil engineer lays out the physics behind Dali’s crash into the Francis Scott Key Bridge pier.
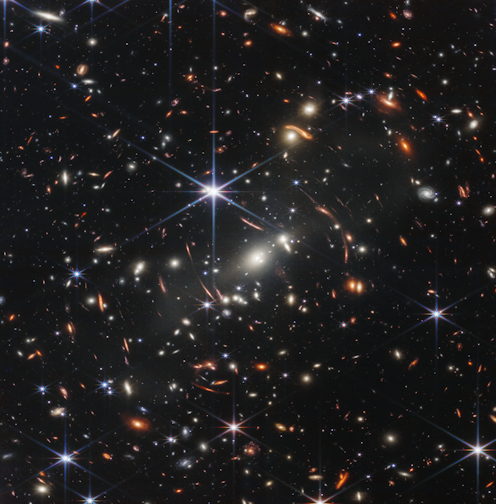

Now out in space for more than two years, the James Webb Space Telescope is a stunningly sophisticated instrument.
