Picture a reclusive man, dripping with sweat all night in a dark lab, illuminated only by crackling sparks that periodically leap from enormous machines and cast a purple glow across his face. This was Nikola Tesla, the archetype of the mad scientist. His inventions fill the world around us; they are instrumental to our modern electrical grid. They are quiet, reliable, invisible machines.
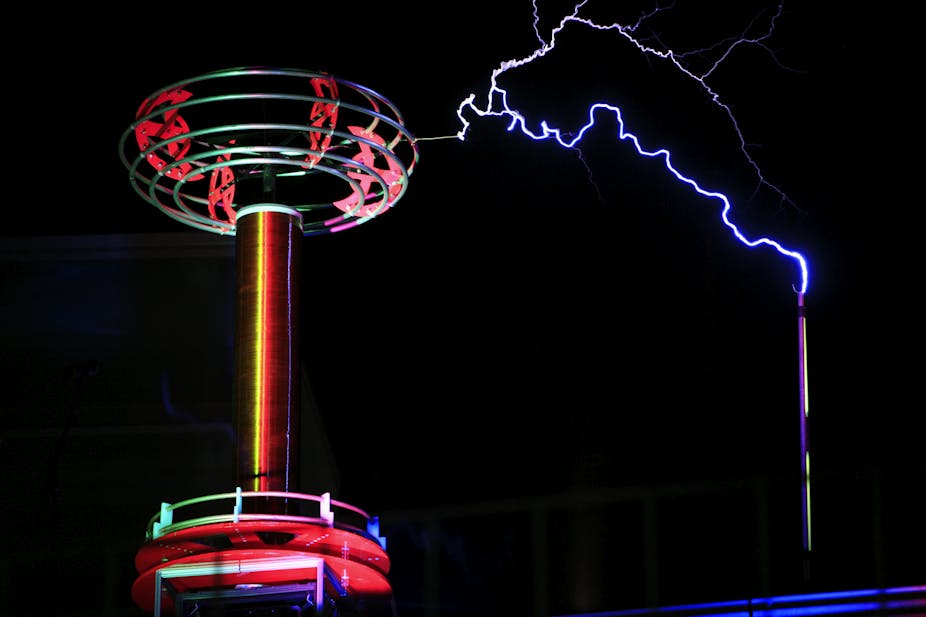
Perhaps his most famous invention is the Tesla coil – a contraption that produces beautiful flying arcs of electrical energy. It was invented by Tesla in an attempt to transmit electricity wirelessly.
Transformer in action
The principles behind the Tesla coil are relatively simple. Just keep in mind that electrical current is the flow of electrons, while the difference in electric potential (voltage) between two places is what pushes that current. Current is like water, and voltage is like a hill. A large voltage is a steep hill, down which a stream of electrons can rapidly flow. A small voltage is like a near-flat plain with almost no water flow.
The power of the Tesla coil lies in a process called electromagnetic induction. This is where a changing magnetic field creates a voltage that compels current to flow. In turn, the flowing electric current generates a magnetic field. When electricity flows through a wound up coil of wire, it generates a magnetic field that fills the area around the coil in a particular pattern.
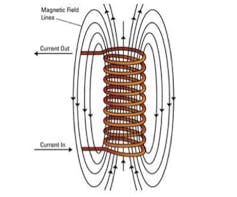
Similarly, if a magnetic field flows through the centre of a coiled wire, a voltage is generated in the wire, which causes an electrical current to flow.
The voltage (“hill”) generated in a coil of wire by a magnetic field through its centre increases with the number of turns of wire. A changing magnetic field within a coil of 50 turns will generate ten times the voltage of a coil of just five turns. (However, less current can actually flow through the higher potential, to conserve energy.)
This is exactly how a common alternating current (AC) electrical transformer, found in every home, works. The constantly fluctuating electric current flowing in from the power grid is wound through a series of turns around an iron ring to generate a magnetic field. Iron is magnetically permeable, so the magnetic field is almost entirely contained in the iron. The ring guides the magnetic field (in green to the right) around and through the centre of the opposite coil of wire.

The ratio of coils on one side to the other determines the change in voltage. To go from 120V household wall voltage to, say, 20V for use in a laptop power adaptor, the output side of the coil will have six times fewer turns to cut the voltage to one sixth its original level.
How the coil rolls
Tesla coils do the same thing, but with a much more dramatic change in voltage. First, they employ a pre-made high voltage iron core transformer to go from 120V wall current to roughly 10,000V. The wire with 10,000 volts is wrapped into a large (primary) coil with only a handful of turns. The secondary coil contains thousands of turns of thin wire. This steps up the voltage to between 100,000 and 1,000,000 volts. This potential is so strong that the iron core of a normal transformer cannot contain it. Instead, there is only air between the coils.
The Tesla coil requires one more thing: a capacitor to store charge and fire it all in one huge spark. The circuit of the coil contains a capacitor and a small hole called a spark gap. When the coil is turned on, electricity flows through the circuit and fills the capacitor with electrons, like a battery. This charge creates its own electric potential in the circuit, which tries to bridge across the spark gap. This can only happen when a large amount of charge has built up in the capacitor.
Eventually so much charge has accumulated that it breaks down the electrical neutrality of the air in the middle of the spark gap. The circuit closes for a fleeting second and a huge amount of current blasts out of the capacitor and through the coils. This produces a very strong magnetic field in the primary coil.
The secondary wire coil uses electromagnetic induction to convert this magnetic field to an electric potential so high that it can easily break apart the air molecules at its ends and push their electrons in wild arcs, producing enormous purple sparks. The dome on the top of the device acts to make the secondary coil of wires receive energy more fully from the first coil. With some careful mathematical calculations, the amount of electrical energy transferred can be maximised.
Flying blue streamers of electrons flow off the coil and through the hot air searching for a conductive landing place. They heat the air and break it into a plasma of glowing ion filaments before dissipating into the air or surging into a nearby conductor.
A tremendous light show is generated, as well as a loud buzzing, crackling sound, which can be used to play music. The electrical theatrics are so stunning that Tesla was known to use his device to scare and mesmerise visitors to his lab.
Tesla might not have invented a source of unlimited power, which was one of his goals, but he did design a brilliant machine to demonstrate the sheer power and beauty of electricity.
This article first appeared on RealClearScience.

