First Nations people please be advised this article speaks of racially discriminating moments in history, including the distress and death of First Nations people.
On October 9 1873, George Augustus Frederick Dalrymple reclined in a boat on the glorious North Johnstone River in the coastal Wet Tropics. Dalrymple was in raptures. A riot of palms, bananas, ferns and lilies descended to the waters edge, and large-leafed taro grew in strips along the riverbank over tens of hectares. He came across a large village with rows of neatly made bark and palm leaf huts. Dappled paths led to managed patches of open forest, groves of fruit trees, bananas and yams. Nearby, a small fleet of moored catamarans sat bobbing.
In the colonial literature, there are many such descriptions of beautiful and bountiful pre-European tropical landscapes. It was clear that people had helped create such a rich paradise through their land management
By 1886, many rainforest people of tropical north Queensland had been “dispersed” – killed – and swathes of this biodiversity hotspot began being cleared for sugarcane.
First Nations groups such as Australia’s rainforest people had skilfully managed entire ecosystems over the long term, in what has been termed “ecology on steroids”. These future-making methods protected landscapes from climate change and buffered them against extinction.
Australia’s First Nations did this through the cold and dryness of the last ice age, and as the seas rose through the droughts and floods of the El Niño Southern Oscillation climate cycle.
As we face an uncertain climate future, it’s valuable to look at how people weathered such change.
Decoupling landscape from climate change
When people first came to Australia, the Wet Tropics were not wet. The Pleistocene climate was cool and windy, with mega monsoons and long periods of diabolical drought. If you had looked east from what is now Cairns, you would have seen not oceans and coral atolls, but plains and valleys filled with grasslands and forest. The sea lay tens of kilometres off the continental shelf.
The oldest record of human occupation in Australia is found in the Top End. Here, in a magnificent cave system in Arnhem Land, people prepared a meal of native fruits and processed pandanus using an adaptable toolkit. This meal took place 65,000 years ago, when savannah stretched all the way to the island of New Guinea.
Over thousands of years, Australia’s people developed a vibrant cosmology. For First Nations people Country was sentient. The land was not a mindless resource but part of your family – and came with family obligations. Everyone, whether you were human, an animal, a plant, a river, fire, the sky or wind, was closely watched. People were embedded within ecosystems.
Recently scientists sampled the deep mud of Girraween lagoon in the Top End searching for pollen and charcoal that would provide a window into this deep time.
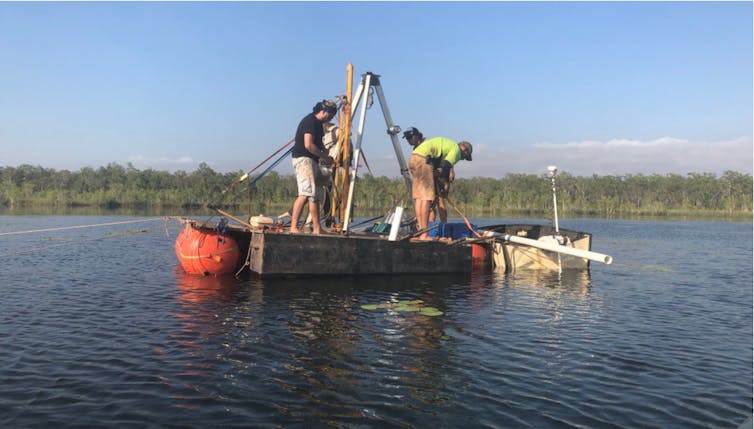

Some 13,000 years ago, the landscape was parched. But as the northern hemisphere ice sheets melted, the seas rose and the monsoons began to return. By the mid-Holocene, between 9,000 and 4,000 years ago, the monsoons were arriving regularly. The lagoon filled up, nestled in a landscape of moisture-loving shrubs and brushed by relatively cool fires.
But then, the climate lurched to one of the long periods of horrendous drought instigated by an El Nino weather system.
Curiously, destructive fires did not follow. The deep mud core showed fire became less, not more, intense, as the forest shaded out the volatile grasses that cause intense fires in savanna. Even as drought increased, the Top End landscape filled with layers of diverse herbs and shrubs, with a variety of trees and groves of monsoon forest closer to the lagoon.
This patterning was likely the handiwork of people taming fire and putting it to work. Through patch burning, they created a rich landscape of diverse habitat that sustained people and created niches for a wide range of species.
Today, a quarter of Australia’s fire-prone savannahs, mostly managed by First Nations peoples, are returning to patchy fire regimes. These reduce the big wildfires associated with European pastoralism and reduce emissions.
Read more: To address the ecological crisis, Aboriginal peoples must be restored as custodians of Country
Extinction busters
Perhaps few places encapsulate the harshness of Australia’s environment more than the Great Sandy Desert. From before the last ice age, the ancestors of today’s Martu people would have witnessed great floods rushing down the Sturt Creek into an extensive lake system, Paruku (Lake Gregory). These lakes were ten times larger than today’s system, ringed by dunes covered in scrubby vegetation and flammable spinifex.
Over perhaps 50 millennia, the Martu used fire to create mosaic landscapes.
In the 1960s, the Martu were forced to leave to make way for nuclear missile tests. Without cultural burning, it took mere years for fuel to build up and large wildfires to incinerate the landscape.
You can see the change clearly. Satellite images and aerial photograhy showed the size of the average fire went from 64 hectares under Martu management to over 50,000 ha by the 1980s.
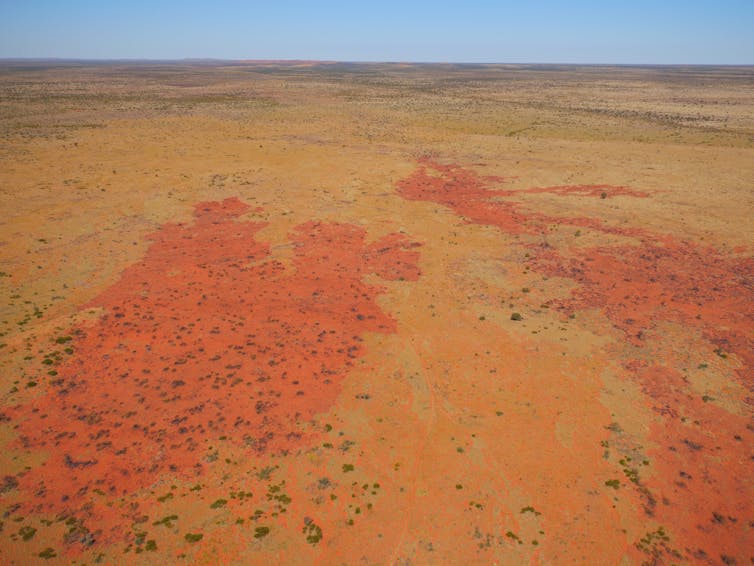

In turn, this drove dramatic shifts to the food web. Over the two decades of Martu absence, ten species of small mammal became locally extinct, including the rufous hare-wallaby, burrowing bettong, bilby, mulgara and brushtail possum. What’s more, 14 mammals, three birds and two reptiles became threatened. Cats, foxes, camels and buffel grass became widespread.
In the 1980s, the Martu were able to return. Back on Country, they worked with scientists to reconstruct pre-1960s food webs from their memories, recalling not only species hunted, but rich detail of the behaviour, interactions and life histories.
Today, Indigenous Protected Areas covering millions of hectares have been added to the national estate. The Western Desert Martu Ranger program manage 6.5 million hectares.
This return to First Nations management is long overdue, as human-made climate change intensifies. We will need to relearn these ancient techniques of managing country on a broader scale to cope with the changes to come.
Read more: Indigenous knowledge and the persistence of the 'wilderness' myth

