
Articles sur Seniors
Affichage de 1 à 20 de 95 articles

When boomers pick out an article of clothing for the elderly, they consider not only the practical aspects like comfort and ease of care, but also how the item will make them feel.

New research has found that immigrants’ income falls behind once they turn 50 and their disadvantage only gets worse as they continue to age.

Contrary to assumptions that seniors are technologically averse, many older adults now show remarkable agility in navigating digital media.
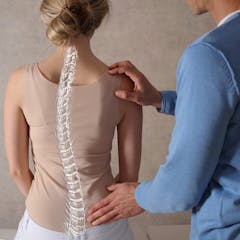
Scoliosis is a treatable condition, but only if detected early. Greater awareness of the condition and its dynamics will greatly aid in patient care moving forward.

Automobile technology provides opportunities for older drivers to maintain their independence and autonomy, but cars need to be designed with their needs in mind.

Dementia does not manifest solely as a memory problem. People with dementia can also experience issues with learning, comprehension and judgement, but they may also experience changes in behaviour.

Publicly funded primary and home care should be accessible to all older adults, regardless of where they live.

An accurate prediction of survival can enable earlier conversations about preferences and wishes at the end of life, and earlier introduction of palliative care.

Children absorb these stereotypes from a young age. And ageism is all around us.

While both nursing homes and home care impose financial burdens, their differing structures can influence how older Canadians save money.

Dementia care in South Asian households is shaped by cultural, familial and societal forces that bring benefits and challenges.

While there is no guarantee of warding off cognitive decline, encouraging people to be physically, mentally and socially active could potentially keep a significant number of dementia cases at bay.

Health and climate change researchers explain the risks and why older adults, even those in northern states, need to pay attention.

What is life like at 100? Centenarians shared their joys and future hopes with a team of Saskatchewan researchers.

Intergenerational Day serves as a reminder of what the old and young can learn from one another, as well as the benefits that come from connecting with others.

The challenging realities surrounding end-of-life care are especially difficult for older people experiencing homelessness, who have more barriers to accessing hospice care.

COVID-19 is the third-leading cause of death in Canada, but it’s older people who are dying. That we accept this and carry on as if the pandemic is over reveals our ageism: We don’t value older people.

New research affords a rare window into the circumstances and needs of a potentially very vulnerable group that until now has remained largely invisible: people with dementia who have no close kin.

To reduce ageist perceptions of older people, we should encourage collectivist norms and the importance of acting for the common good.

Repeated storytelling from elderly relatives doesn’t necessarily always signal age or cognitive decline. It’s about conveying memories and values to a new generation.
